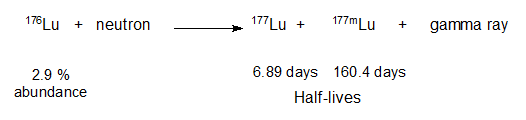[Note: This is an updated post from the original posted one year ago.]
March 22, 2022. Swiss drugmaker Novartis has released Pluvicto, “the first FDA-approved targeted radioligand therapy (RLT) for eligible patients with mCRPC that combines a targeting compound (ligand) with a therapeutic radioisotope (a radioactive particle). Pluvicto is expected to be available to physicians and patients within weeks.“
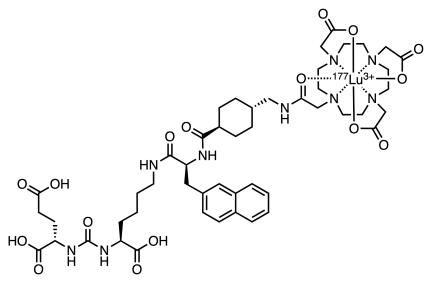
Pluvicto features a chelated 177Lutetium ion (half-life 6.7 days) which is the source of the molecule’s radioactivity. Lutetium is the heaviest of the lanthanide elements and the name comes from the Latin Lutetia Parisiorum which was the predecessor to the city of Paris, France.
Pluvicto has been approved in the US for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. Several things are notable about the Pluvicto molecule. The molecule contains a PSMA-specific peptidomimetic feature with an attached therapeutic radionuclide, where PSMA stands for Prostate Specific Membrane Antigen. Peptidomimetic refers to a small chain that resembles a stretch of protein forming amino acids. This peptidomimetic fragment, which interestingly contains a urea linker, is designed as the tumor targeting piece of the drug. Connected to it is a chelated radioactive 177Lutetium cation (below, upper right). The tumor targeting fragment binds to the cancer cell. While bound to the cell, the short-lived radioisotope undergoes two modes of decay. The 177Lu has two decay modes. One emits a medium energy beta particle (Eβmax = 0.497 MeV) which is limited to a maximum of 0.670 millimeters of travel. This is the kill shot that will damage the attached and nearby target cells. The short path length of the beta ray in vivo limits the extent of surrounding damage by any given decay. Once the 177Lu emits a beta particle it becomes 177Hafnium.
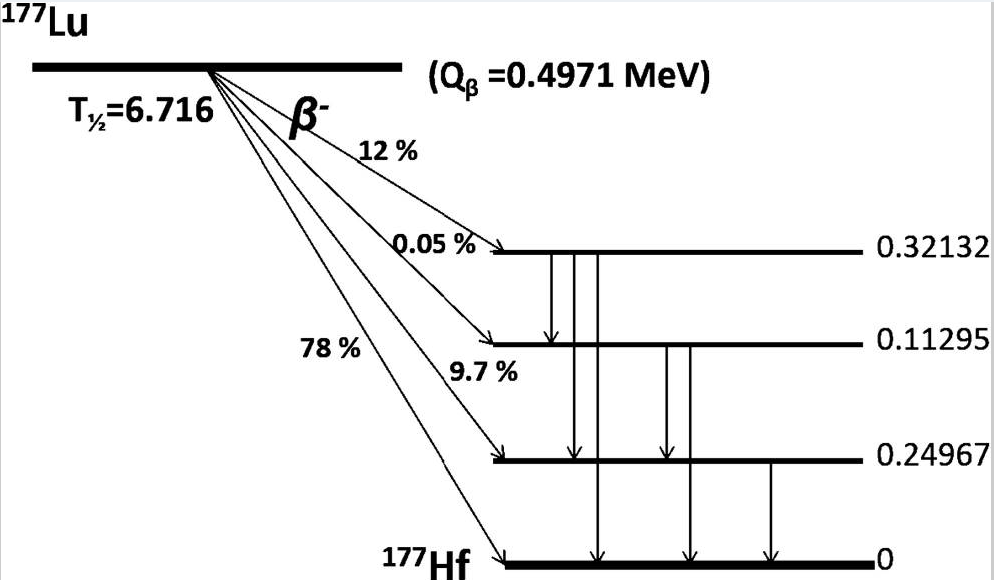
The other mode of 177Lu decay is gamma emission by 177mLu, a nuclear isomer or metastable form of 177Lu. Gamma radiation is much more penetrating than beta radiation. The gammas can be detected from the outside of the patient allowing monitoring of dose and location of the drug. Even though gamma rays are more penetrating than beta rays, they produce many fewer ion pairs per centimeter as they traverse the tissue making them less effective per photon in tissue destruction compared to alpha and beta particles. For instance, alpha particles from therapeutic radionuclides like 223Radium used to treat prostate cancer are much more destructive because they produce many ion pairs per centimeter.
A Small Side-Track into Radon Decay
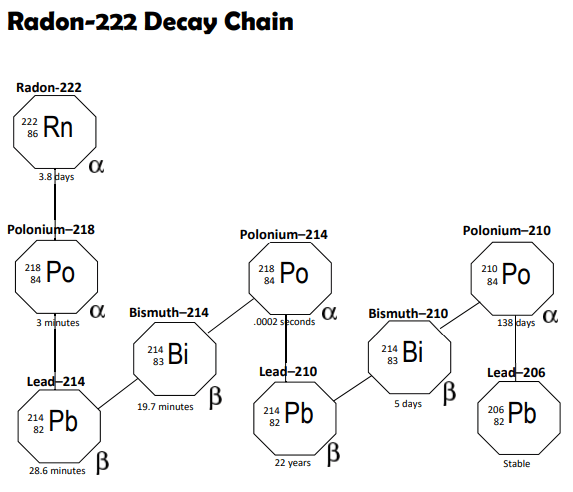
Not all radioactive isotopes are alike. Some, like 177Lu, offer only a single decay event while others are part of a domino series of decays. The decay of naturally occurring 222Radon begins a series of decay events (Radon’s daughters), with some decays being quite rapid, multiplying the radiological effect per initiating atom. Inhaling an alpha emitter like 222Radon is a gamble. Until the 222Rn decays, it is just an inert noble gas. But when it alpha decays in your lungs, it is converted to the 218Polonium which alpha decays to 214Lead which beta decays to 214Bismuth which beta decays to 214 Polonium which alpha decays to 210Lead which beta decays to 210Bismuth which beta decays to 210Polonium which alpha decays to stable 206Lead where the chain stops. Each of the daughter products is a reactive, nonvolatile metal.
Neutron Activation of 176Lutetium
How does one obtain 177Lu? There are two pathways of nuclear chemistry that can be used, each with plus and minus attributes. The easiest pathway to execute would be the absorption of a thermal neutron by the lighter lutetium isotope 176Lu followed by a gamma emission from the new 177Lu. Gamma emissions result from metastable coproduct 177mLu that is in an excited state. It can de-excite by losing the excited state energy by the release of a gamma photon.
An excellent review of this topic is by: Ashutosh, Dash; Maroor, Raghavan; Ambikalmajan, Pillai; and Furn F. Knapp, Jr. Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2015 Jun; 49(2): 85–107. doi: 10.1007/s13139-014-0315-z.
Where does one get thermal neutrons and what is “thermal” about them? Thermal neutrons are produced in a water-cooled nuclear reactor. It turns out that nature has bestowed a wonderful gift on 176Lu. It has a very large neutron capture cross section of 2090 barns for producing 177Lu. The metastable 177mLu isomer has a cross section of only 2.8 barns.
The unit “barn” is the unit of the effective target area of a nucleus and is equivalent to 10-28 m2, or 100 square femtometers. The capture cross section of a nucleus is dependent on the energy (or temperature) of a neutron and is proportional to the probability of a collision. Here is a brief reference on nuclear cross sections. The colorful etymology of the term “barn” is recalled here.
For comparison, the capture cross section of 239Plutonium is on the order of 750 barns with 0.025 electron volt neutrons. We can see that the capture cross section of the 176Lu is much larger than that of 239Pu. The word “thermal” comes from the kinetic energy corresponding to the most probable speed of a free neutron at a temperature of 290 K (17 °C or 62 °F).
The transmutation [176Lu + 0n —> 177Lu + 177mLu] is clean and direct with no other chemical elements to interfere. With its large capture cross section,176Lu is well suited to absorb a neutron. The down side is that the isotopic abundance of 176Lu is only 2.8 %. The other 97.2 % of Lu can also undergo neutron activation leading to chemical and radiological contamination of the desired 177Lu. Isotopic separation of 176Lu from the other Lu isotopes is difficult and not very scalable. By the way, the lutetium is neutron activated as the refractory oxide, Lu2O3. These lanthanide oxides are simple to prepare and can be dissolved in acid afterwards to produce Lu3+ cation for further chemistry.
Neutron Activation of 176Ytterbium
The other major channel to 177Lutetium is from neutron activation of 176Ytterbium, 176Yb. Generally speaking, the heavy lanthanides like Yb and Lu are less abundant than the light lanthanides on the left side of the series. All of the lanthanides have a 3+ oxidation state and similar ionic radii making them difficult to chemically separate, where “difficult” means that numerous steps are needed in purification often resulting in low yields. A few of the lanthanides have oxidation states other than +3. It turns out that Yb3+ can be selectively reduced by chemistry to Yb2+ in the presence of Lu3+ using sodium amalgam as the reductant. This happy fact allows for plausible chemical separation of Lu from Yb. Furthermore, Yb will amalgamate while Lu does not.
A Google search of Pluvicto or 177Lutetium will produce many good links of a technical and non-technical nature.
Pluvicto, PSMA-targeted radiotherapy
(lutetium 177Lu vipivotide tetraxetan)
for PSMA-positive prostate cancer
7.4 GBq (200 mCi) IV Q6W up to 6 doses